
The most well-known theories are probably those of supply and demand, but you will also learn a number of other theories. Microeconomics and macroeconomics are explained based on theories and models. The model represents all of the actors in an economy as either households or firms (companies), and it divides markets into two. Though you can sometimes figure out the right answer without using a model at the introductory level, if you continue to study economics, before long you will run into issues and problems that you will need to graph. One of the main basic models taught in economics is the circular-flow model, which describes the flow of money and products throughout the economy in a very simplified way.Instead, they use the graph of the theory to figure out the answer. In other words, the flow of money income will not always continue at a constant level. It may, however, be pointed out that this flow of money income will not always remain the same in volume. We will mostly be using graphs in this course.) Economists don’t figure out the answer to a problem and then draw a graph to illustrate it. This circular flow of money will continue indefinitely week by week and year by year. Theories are expressed by economists in the form of diagrams, graphs, or even mathematical equations.
Using the theory, they derive insights about the issue. The first thing they do when they see a problem or issue in economics is to go through the theories they know to see if one fits.
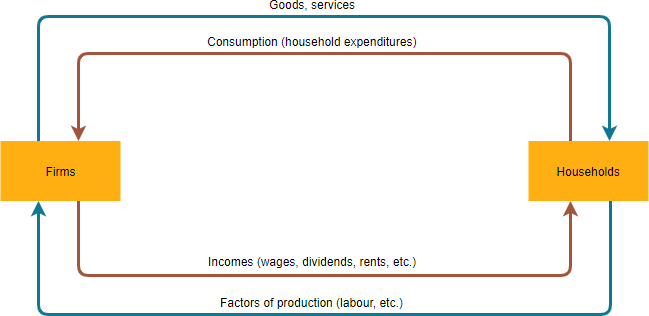
The two arrows A and B represent the two sides of the product market.Households purchase goods and services, and companies earn revenue from that.Decrease in GDP growth means that the output of an economy is still growing but at a slower rate.
Decrease in GDP means that output of an economy is actually falling. You must also know the distinction between a decrease in GDP and a decrease in GDP growth. Increasing government expenditure and shrinking tax revenue.Recession occurs when GDP falls for at least two consecutive quarters, hence takes place shortly after booms/peaks (right when GDP begins decreasing): Learn the meaning of the terms 'money flow' and 'real flow.' Find out how they relate to each other in the circular flow of income economic model.Growing tax revenue (possibly falling government expenditure on e.g.Recovery takes place after troughs right when GDP starts growing again:.Shortage of factors of production (most probably labour).The business cycle also known as the trade cycle shows growth of an economy around the long term trend (dashed line) measured by changes in GDP.Ĥ facts to know about the business cycle:
CIRCULAR FLOW DIAGRAM FULL
The income in the circular flow is always equal to the national income, however this equilibrium does not necessarily mean the economy is at full employment. Income going into the flow is called injections and income going out of the flow is known as leakages.Įquilibrium of national income is reached when (planned) Injections = (planned) Leakages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
